Saab Automobile AB is an automobile manufacturer from Sweden. It was founded in 1945 when its mother company, SAAB AB, started on creating a small automobile. Currently, Saab Automobile AB is inactive in the markets and production.

The first model that was successfully finished under the Saab brand is the Saab 92 which was launched in 1949. After joining another company named Scania- Vabis, the Saab 900 was created. During that time, the Saab 900 was the best-selling model.
In 1989, the division of Saab-Scania which focuses on automobiles decided to restructure the company, hence Saab Automobile AB was founded. Matter-of-factly, General Motors, a giant in the automobile industry, bought half the company in 2000. They invested $600 Million for this and after some time, GM bought the whole company already.
Related Other Swedish Automobile Manufacturer Koenigsegg Cars
This made Saab Automobile as a whole subsidiary of GM. Ten years after, GM sold this division to Spyker Cars N.V., a Dutch vehicle manufacturer. Only a year after, Spyker Cars N.V. faced a bankruptcy issue when a Chinese association failed to purchase the whole subsidiary. GM then blocked the purchase to avoid the Chinese company from acquiring Saab Automobile.
In 2012, a new company named National Electric Vehicle Sweden bought Saab Automobile and carried it out of bankruptcy. After a year, Saab Automobile started manufacturing cars again, starting with the Nevs Saab 9-3. Unfortunately, NEVS was declined to continue the manufacturing under the Saab brand, and from then on, no more cars were made for the Saab branding.
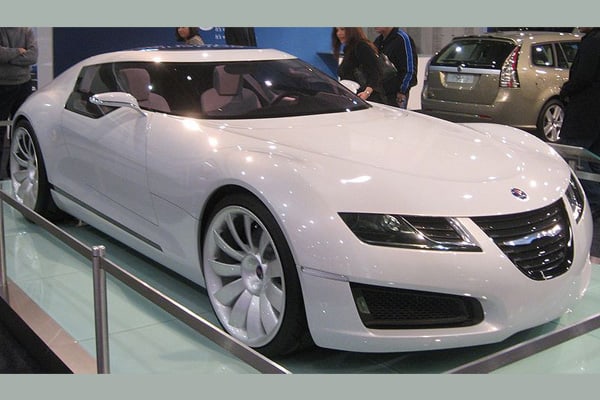

Image source: wikimedia.org
Even though there were several transfers of the Saab brand, it became popular to the market. Under GM, they were able to pull out the units Saab 9-5, Saab 9-3 Sport Combi, and the Saab Aero-X. In the motorsport limelight, Saab was also able to compete in the Trans Am Series in 1966. They won several awards from their drivers including Tom Trana, Per Eklund, and Simo Lampinen.
The Full Saab Models
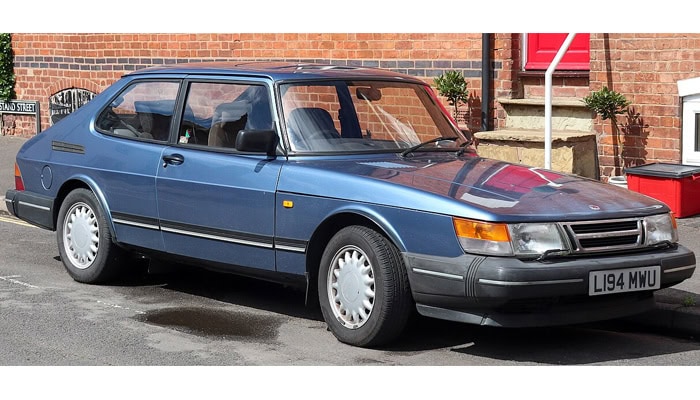

The Saab 900 is one of the most iconic models in the history of Saab, a Swedish car manufacturer known for its distinctive engineering and unique design. Produced from 1978 to 1998, the Saab 900 embodied the company’s focus on safety, innovation, and functionality. The 900’s reputation for reliability, quirky styling, and turbocharged performance set it apart from other cars of its era, making it a cult favorite that still enjoys a loyal following today.
Early Development and Launch (1978-1993):
The Saab 900 was introduced in 1978 as a successor to the Saab 99, sharing much of its predecessor’s platform but with significant improvements. Available in both sedan and hatchback variants, the Saab 900 stood out due to its unique, elongated front end, which was designed to accommodate the company’s turbocharged engines and enhance safety through better crash performance. This design became a hallmark of Saab automobile models.
In terms of engineering, the Saab 900 was innovative, featuring a front-mounted, longitudinally positioned engine. This was unusual for a front-wheel-drive car at the time. The 900 was also known for its strong emphasis on safety, with features like reinforced bumpers, side-impact protection, and a cabin designed to minimize injuries in a crash. These design decisions reflected Saab’s origins in aircraft manufacturing, where safety and precision were paramount.
Turbocharged Legacy:
One of the most defining features of the Saab 900 was its pioneering use of turbocharged engines. The 900 Turbo, introduced in 1978, played a critical role in bringing turbocharged technology to mainstream cars. At a time when most manufacturers were still focusing on naturally aspirated engines, Saab offered turbo engines that improved performance without sacrificing fuel economy.
The turbocharged Saab 900 models quickly became popular for their spirited driving experience, characterized by strong acceleration and excellent handling. The 900 Turbo also helped build Saab’s reputation as a “driver’s car”, combining practicality with performance. This focus on turbo technology set a trend for future Saab automobile models, which continued to innovate in this area.
The Convertible Revolution (1986-1994):
The Saab 900 Convertible, introduced in 1986, became one of the most recognizable variants of the model. At a time when convertibles were losing popularity due to safety concerns, Saab successfully reintroduced the format by engineering a robust rollover protection system. The 900 Convertible combined the sporty performance of the Turbo with the open-air freedom of a convertible, making it an instant hit, especially in the U.S. market.
This version of the 900 helped redefine the image of Saab, not just as a practical, safety-oriented brand but also as a manufacturer that could deliver fun and style. The convertible was often seen as a symbol of success and individualism, further enhancing the model’s appeal.
Second Generation (1994-1998):
In 1994, Saab introduced the second-generation 900, which was developed after General Motors (GM) acquired a 50% stake in the company. While the new generation was built on a platform shared with GM, it retained much of Saab’s distinct character. The second-generation 900 featured modernized styling, updated technology, and new engine options, including a V6. However, some purists felt that it lacked the quirky charm of the original 900 models.
Despite these concerns, the second-generation 900 continued to sell well, especially in Europe and North America, thanks to its blend of performance, safety, and comfort. The model was eventually replaced by the Saab 9-3 in 1998, marking the end of the 900 nameplate.
Legacy and Impact:
The Saab 900 left a lasting legacy in the automotive world. Its emphasis on safety, turbocharging, and innovative design influenced many of the Saab automobile models that followed. For car enthusiasts, the 900 remains a symbol of Saab’s unique approach to car manufacturing—a blend of practicality, innovation, and individuality.
Today, the Saab 900 continues to have a dedicated fan base, with many original models still on the road. Collectors and Saab aficionados often seek out well-preserved 900s, particularly the Turbo and Convertible variants, which are regarded as timeless examples of automotive design.
Conclusion:
The Saab 900 is more than just a car—it’s a testament to Saab’s legacy as a pioneering car manufacturer that prioritized safety, performance, and innovation. Its role in popularizing turbocharged engines and redefining the convertible market cemented its place in automotive history. As enthusiasts look back on the evolution of Saab automobile models, the 900 stands out as one of the most influential and beloved cars in the brand’s lineup.

Image source: wikipedia.org
The Saab Sonnett III is the third generation of the Saab Sonnett, an automobile designed and manufactured by Saab, a Swedish automaker. This was manufactured from 1955 to 1957. The Sonnett III is an overhauled version of the V4. It was produced from 1970 to 1974.
More About Sonnett III on Wikipedia
- Saab 92
- Saab 95
- Saab 96
- Saab 99
- Saab 9-3
- Saab 9-5
- Saab Aero-X
- Saab 9-2
- Saab 93
- Saab GT750
- Saab Sonett I
- Saab Sonett II
- Saab Sport
- Saab Formula Junior
- Saab 90
- Saab 9000
- Saab 9-2X Linear
- Saab 9-4X
Saab’s list of Concept car models:
- Saab Ursaab
- Saab Monster
- Saab 60
- Saab Quantum
- Saab Catherina
- Saab 9000 Cabriolet
- Saab MFI13
- Saab Toad
- Saab 98
- Saab EV-1
- Saab Viking
- Saab Prometheus
- Saab 9XX
- Saab 9-X
- Saab PhoeniX
Other Saab models
- Saab 9-6X
- Saab 900 Talladega
- Saab 9-7X
- Saab 9-2X
- Saab 900 Convertible
- Saab 9-X Biohybrid
- Saab Sonett
- Saab 9-X Air
- Saab 600
- Saab Convertible
Video of Saab Car Models
Photos of Saab’s Different Types of Cars
(Photos Courtesy of https://en.wikipedia.org/)






























Saab on Wiki
Swipe to see other trivia